39 bacterial cell without labels
Morphology, Different shapes of bacterial cell - BYJUS Bacteria cell is 10 times smaller than the human cell; The diameter of a bacteria cell is ~1µm (10-6 m) The outer covering of a bacteria cell is the cell wall, which is rigid and provides structural integrity; The bacteria cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan or murein; Different shapes of bacteria cell are the characteristic feature of a bacteria species; Bacteria cells may contain external appendages like cilia, flagella, etc. Bacteria can be photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs or parasites Smart food label can identify bacteria without opening the package ... Smart food label can identify bacteria without opening the package. by Victoria Corless | Sep 10, 2020. Food-safe microneedles incorporated into a new smart label can effectively collect samples from packaged food and inform consumers about its quality in real time. Velcro-like food sensor, made from an array of silk microneedles.
Metabolic RNA labeling for probing RNA dynamics in bacteria Aiming to develop nucleoside analogs compatible with bacterial RNA labeling, we first set out to evaluate the two nucleoside analogs widely used in eukaryotic cells. E. coli cells were incubated with 4SU or EU at varied concentrations for 2 h, which resulted in no detectable labeling even at high concentrations ( Supplementary Figure S1A, B ).

Bacterial cell without labels
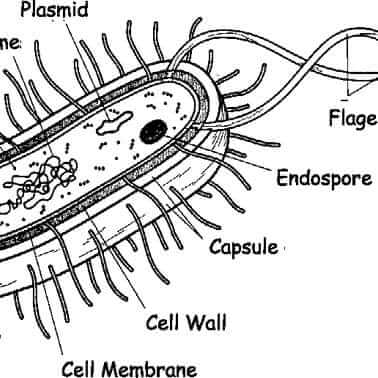
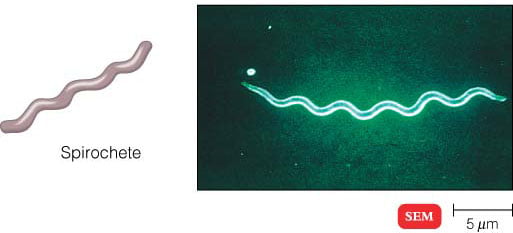
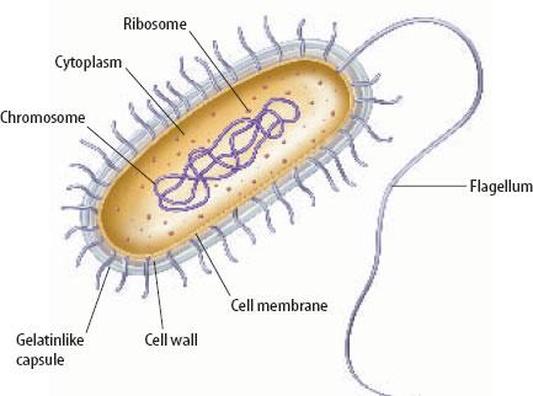
Structure of Bacterial Cell (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion In this article we will discuss about the Structure of Bacterial Cell. Bacteria (sing. bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission. They do not possess nuclear membrane and the nucleus consists of a single chromosome of circular double-stranded DNA helix (Fig. 1.1). Flagella: 3 Common Bacteria Shapes - ThoughtCo Spirochetes (also spelled spirochaete) bacteria are long, tightly coiled, spiral-shaped cells. They are more flexible than spirilla bacteria. Examples of spirochetes bacteria include Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease and Treponema pallidum, which causes syphilis. Vibrio Bacteria Visualization and In Situ Ablation of Intracellular Bacterial ... - PubMed Moreover, TPEPy-d-Ala can effectively ablate the labeled intracellular bacteria in situ owing to covalent ligation to peptidoglycan, yielding a low intracellular minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 20±0.5 μg mL -1 , much more efficient than that of a commonly used antibiotic, vancomycin.
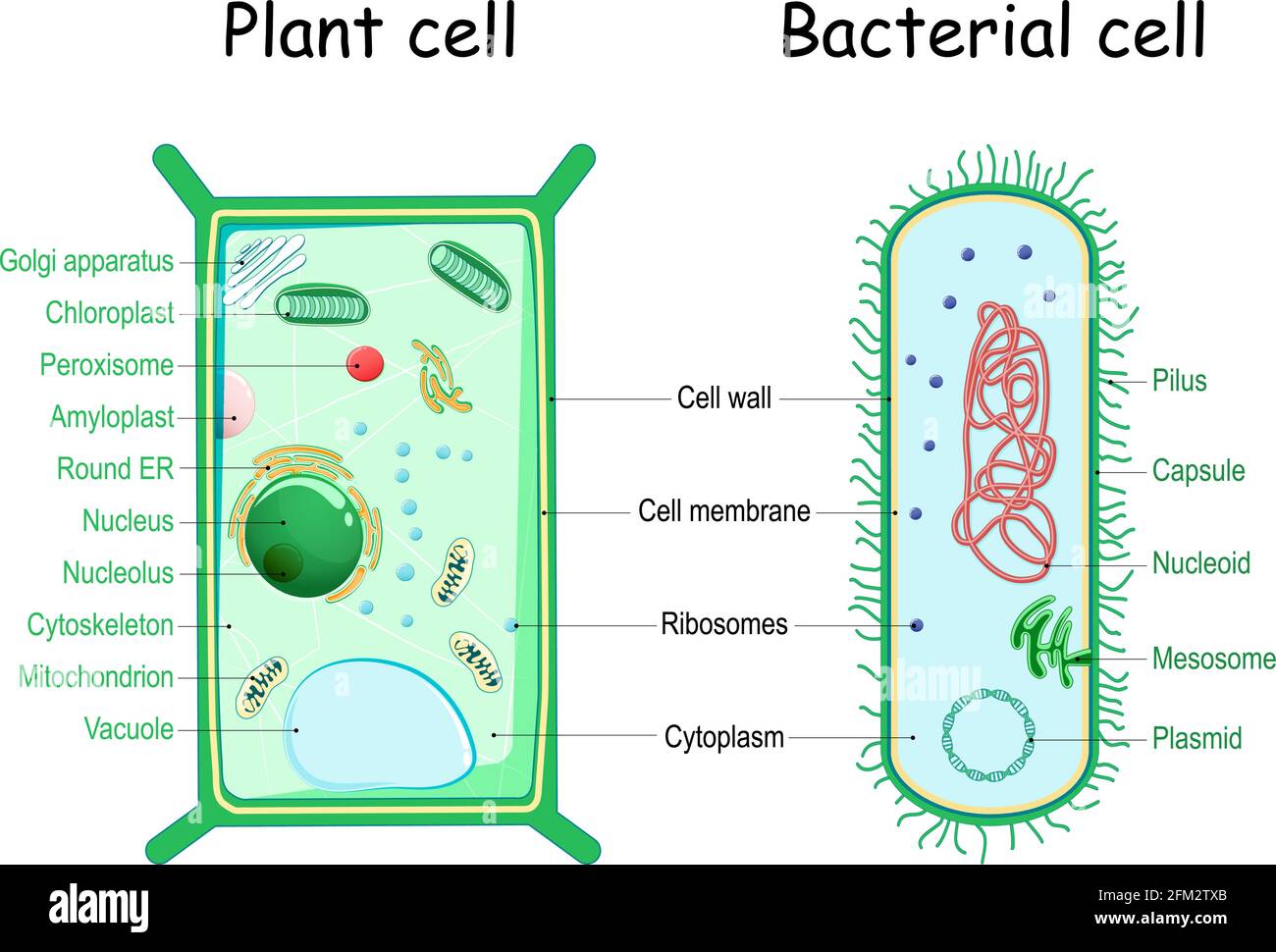
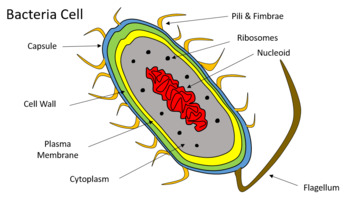
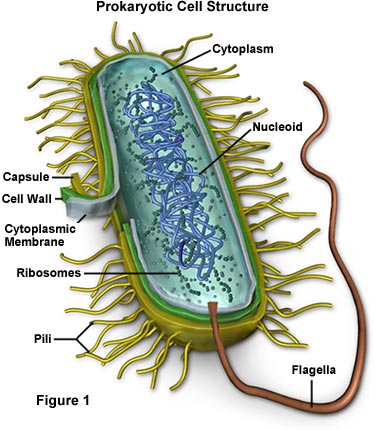
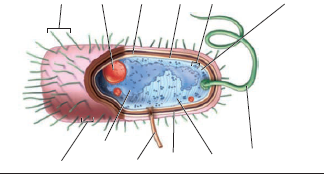
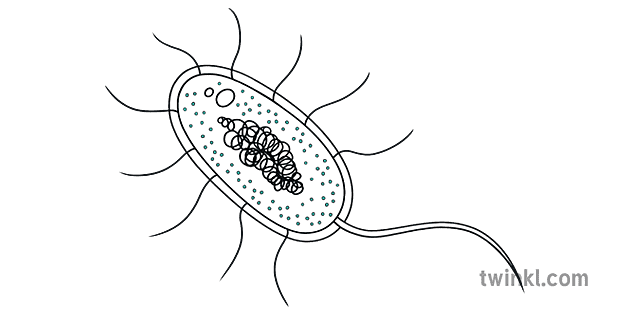
Bacterial cell without labels. Bacterial Cell: Structure and Components | Microbiology Bacterial cells (prokaryotic cells) are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 3.2. They consists of various cell surface structures, cell wall, plasma membrane, many cytoplasmic inclusions, and the bacterial chromosome (nucleoid). Except some, all structures do not occur in every genus. Bacterial cells with labels. - Healthclinic Bacterial cells with labels. The spheroid or ovoid or coccus. Bacillus. Vibrio. Spirillum. Spirochaete. Bacterial cells with labels. Bacteria cell anatomy Bacterial cells are microscopic unicellular organisms. The unit of measurement of bacteria is the micrometer (μm) and it is 1/1000 of a millimeter (.001μm). Phases of the Bacterial Growth Curve - ThoughtCo The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. There are four distinct phases of the growth curve: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death. The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing. The exponential or log phase is a time of ... Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification - BYJUS Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions. Such organisms are called extremophiles.
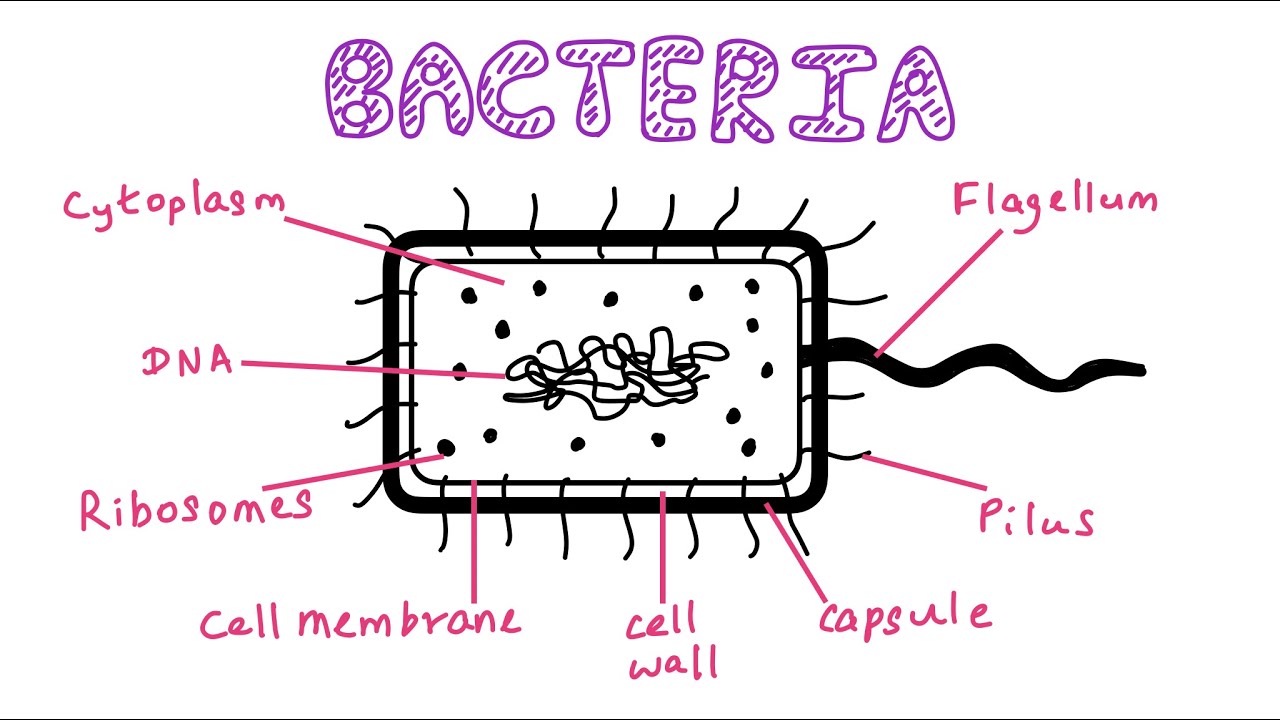
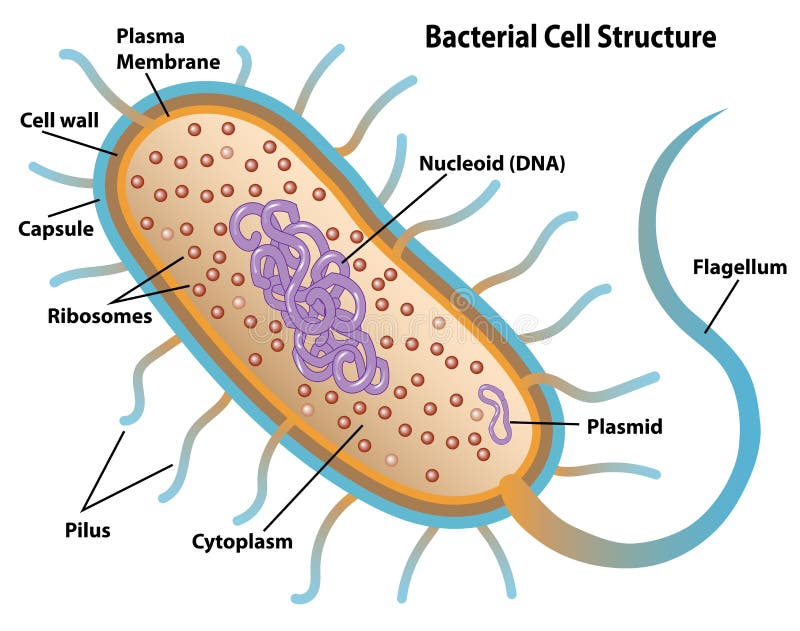
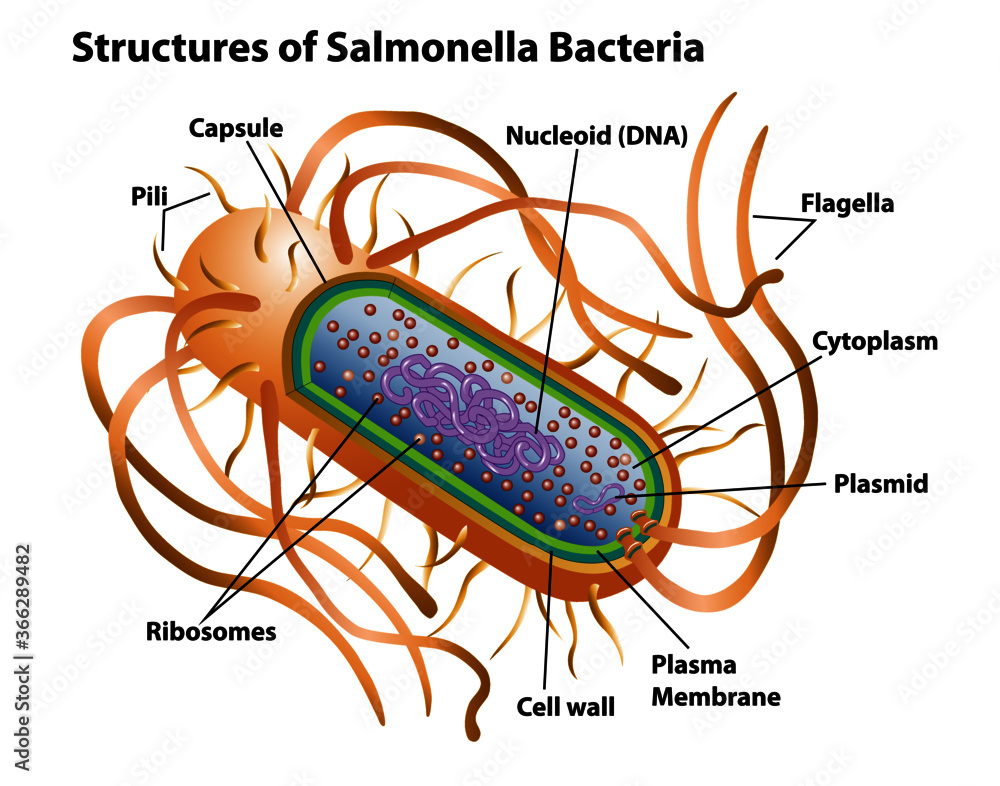
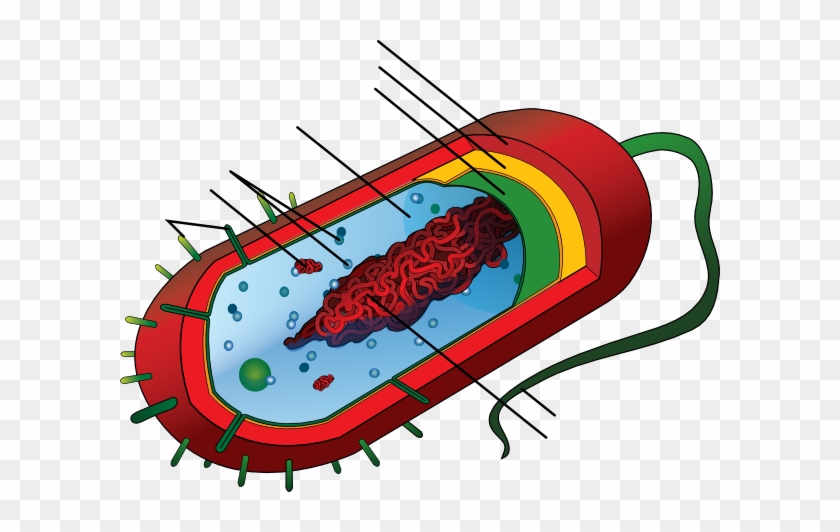
Bacterial cell structure and function - Online Biology Notes Bacterial are unicellular prokaryotic organism. Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosome, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, peroxisome, glyoxysome, and true vacuole. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus. Bacterial Cell wall: Structure, Composition and Types Cell wall is an important structure of a bacteria. It give shape,rigidity and support to the cell. On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group ie. Gram Positive and gram negative. Types of cell wall 1. Gram positive cell wall Cell wall composition of gram positive bacteria. Peptidoglycan Lipid Teichoic acid Bacterial Cell: Definition, Types, Structure, and Facts - Research Tweet Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms. The cell structure is less complex than that of different creatures as there are no core or film-bound organelles. A few bacteria have an additional circle of hereditary material called a plasmid. The plasmid frequently contains qualities that give the bacterium some benefit over different bacteria. Flagella: Structure, Arrangement, Function - Microbe Online Flagella: Structure, Arrangement, Function. Flagella (singular, flagellum) are the locomotory structures of many prokaryotes. Most protozoa and some bacteria are motile. Protozoa use flagella, cilia, or pseudopods, whereas motile bacteria move only using flagella. The flagellum functions by rotation to push or pull the cell through a liquid medium.
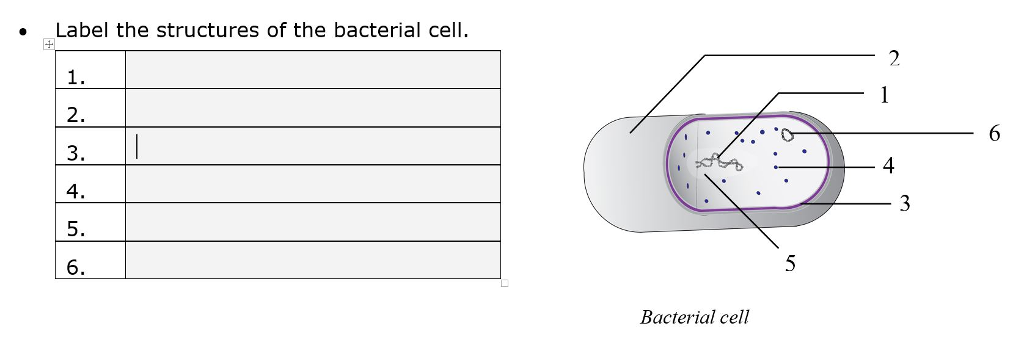
Labeling a bacterial cell 'jacket': Team invents scientific method to ... Labeling the cell 'jacket' Now back to that three to five pounds of bacteria we carry around... Much of the weight comes from the bacteria's cell walls, or "jackets," as Grimes refers to them.... Bacterial Cell Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Cytoplasm Water-based solution filling the entire cell Ribosomes Tiny particles composed of protein and RNA that are the sites of protein synthesis Nucleoid Composed of condensed DNA molecules. Cell Membrane A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials in and out of the cell S Layer Gram-negative bacteria- cell wall, examples, diseases, antibiotics The cell wall of gram-negative bacteria is complex having a thin layer of the peptidoglycan layer of 2-7nm and a thick outer membrane of 7-8nm thick. Microscopically, there is a space that is seen between the cell membrane and the cell wall, known as the periplasmic space made up of periplasm. However it is found in both Gram-negative and Gram ... Can anybody recommend a method for FITC labeling of bacteria B. Preparation of FITC-labeled bacteria. 1. Harvest bacterial cells by centrifugation at 10,000 x g and 4°C for 5 min. 2. Resuspend bacterial cells in 1 ml of 0.1 M sodium bicarbonate buffer ...
Different Size, Shape and Arrangement of Bacterial Cells Bacilli (or bacillus for a single cell) are rod-shaped bacteria. Spirilla (or spirillum for a single cell) are curved bacteria which can range from a gently curved shape to a corkscrew-like spiral. Many spirilla are rigid and capable of movement. A special group of spirilla known as spirochetes are long, slender, and flexible. Arrangement of Cocci
Bacteria in Microbiology - shapes, structure and diagram - Jotscroll Bacteria Cell Wall. The cell wall of bacteria is located at the inner side of the capsule. It is usually rigid and surrounds all eubacterial cells. Most bacteria have a cell wall; there are some that have no cell walls such as mycoplasmas bacteria and Chlamydia. Functions of the bacteria cell wall. Bacteria cell wall prevents osmotic lysis
The Bacterial Cell Envelope - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Accordingly, E. coli and other enteric bacteria must have a cell envelope that is particularly effective at excluding detergents such as bile salts. This need not be a pressing issue for other Gram-negative bacteria, and their envelopes may differ in species- and environmentally specific ways.
Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman ... - Nature Raman optical spectroscopy promises label-free bacterial detection, identification, and antibiotic susceptibility testing in a single step. However, achieving clinically relevant speeds and...
Label-free bacterial imaging with deep-UV-laser-induced native ... A DUV (<250-nm) source enables the detection of microbes in their native state on natural materials, avoiding background autofluorescence and without the need for fluorescent dyes or tags. We demonstrate that DUV-laser-induced native fluorescence can detect bacteria on opaque surfaces at spatial scales ranging from tens of centimeters to micrometers and from communities to single cells.
Bacterial cells - Cell structure - Edexcel - GCSE Combined Science ... Bacterial cells Bacteria are all single-celled. The cells are all prokaryotic. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes. Larger bacterial...
Interactive Bacteria Cell Model - CELLS alive Cell Wall: Composed of peptidoglycan (polysaccharides + protein), the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a bacterial cell. The three primary shapes in bacteria are coccus (spherical), bacillus (rod-shaped) and spirillum (spiral). Mycoplasma are bacteria that have no cell wall and therefore have no definite shape. Outer Membrane: This lipid bilayer is found in Gram negative bacteria and is the location of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in these bacteria. Gram positive bacteria lack this layer.
Label or Concept - What Is a Pathobiont? - Trends in Microbiology The term ´pathobiont´ has already been widely used to label bacteria that have been linked to a disease merely based on sequence-based correlations with diseased individuals [. 23. ]. This is inherently error-prone as microbial community shifts can also occur as a consequence of disease [. 24.
Metabolic labeling probes for interrogation of the host-pathogen ... FDAAs owe their broad applicability partially to their low molecular weight; labeling of the Gram-negative bacterial cell wall requires passage through the outer membrane, which is markedly less permeable to molecules over a molecular weight of ∼600 Da, such as antibiotics. 64 Indeed, when Hsu et al. 65 compared the labeling of E. coli with FDAAs with molecular weights between 300-700 Da ...
Bacterial Identification| 8 Methods & Tests In Microbiology - Study Read Identification by morphology: This method is to determine the individual bacterial physical appearance. 1. Based on size. Here bacteria are identified based on their physical size. Like small size or big one expressed in microns. For this bacteria are viewed under a microscope to view the size.
Introduction to Bacteria | Let's Talk Science Size of Bacteria. Bacteria are single-celled organisms. This means that each bacterium is made up of only one cell. This is very different from humans, whose bodies are made up of trillions of cells . Bacterial cells are much smaller than human cells. Bacterial cells can measure from about 1 to 10 μm long.
Visualization and In Situ Ablation of Intracellular Bacterial ... - PubMed Moreover, TPEPy-d-Ala can effectively ablate the labeled intracellular bacteria in situ owing to covalent ligation to peptidoglycan, yielding a low intracellular minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 20±0.5 μg mL -1 , much more efficient than that of a commonly used antibiotic, vancomycin.
3 Common Bacteria Shapes - ThoughtCo Spirochetes (also spelled spirochaete) bacteria are long, tightly coiled, spiral-shaped cells. They are more flexible than spirilla bacteria. Examples of spirochetes bacteria include Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease and Treponema pallidum, which causes syphilis. Vibrio Bacteria
Structure of Bacterial Cell (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion In this article we will discuss about the Structure of Bacterial Cell. Bacteria (sing. bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission. They do not possess nuclear membrane and the nucleus consists of a single chromosome of circular double-stranded DNA helix (Fig. 1.1). Flagella:













Post a Comment for "39 bacterial cell without labels"